ESnet’s network is operated as a high-availability network 24 hours per day, 365 days per year, and significant resources are devoted to ensuring its continuous and secure availability. While ESnet is required to deliver “three 9s” — 99.9% availability — we routinely exceed that standard. In fact, sites with redundant connections to ESnet often see 100% availability (zero downtime) over the course of a year.
Our staff continues to work on enhancing the technical systems that benefit both our internal team and external production services, to ensure our performance and reliability continue to stay ahead of demand. In 2023, ESnet’s operational achievements included (but were not limited to) improvements to our tools for gathering, assessing, and studying network performance data, as well as those for automating the setup of devices on the production network. We also laid the groundwork for increased trans-Atlantic connectivity and resilience.

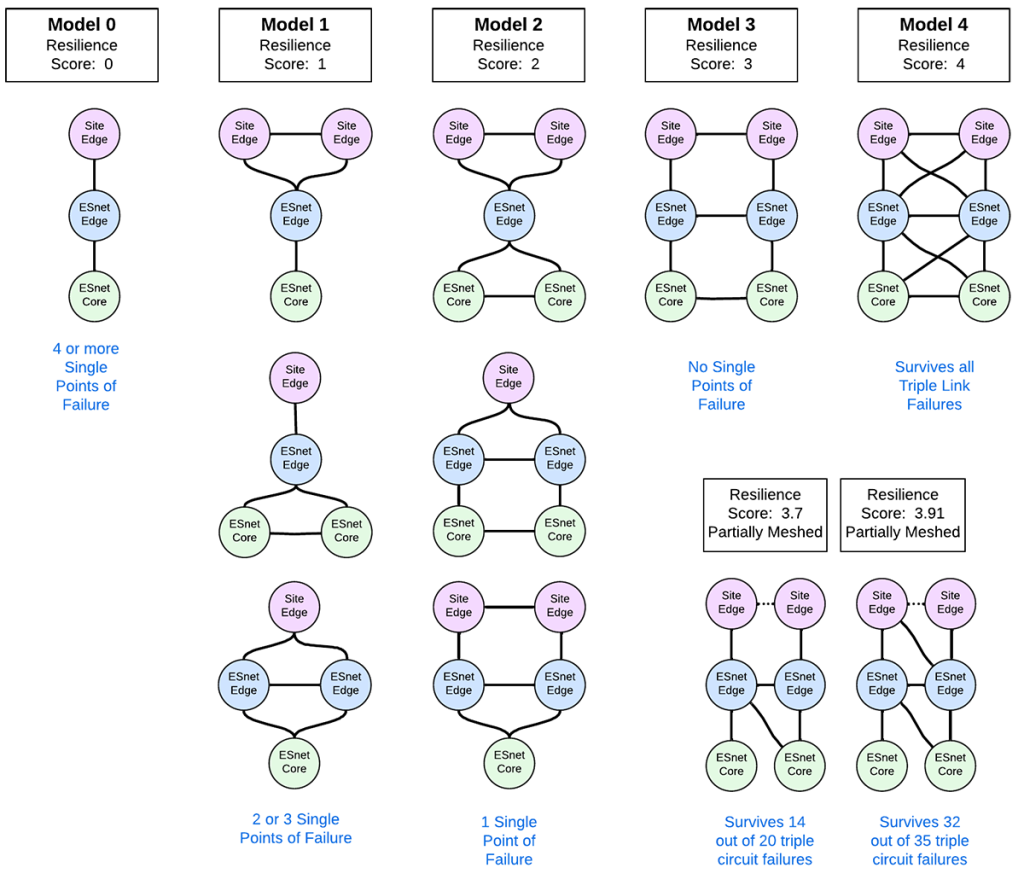
Increasing Site Resilience Across ESnet
As DOE-sponsored science continues to become more distributed and collaborative, the need for a scalable network with high availability, and performance has never been greater. ESnet’s Site Resilience Program (SRP) seeks to ensure that the network can meet these ever-increasing demands by delivering network resilience to each site that meets or exceeds the requirements of that site’s mission.
In 2023, the SRP focused on two key areas:
- Community Awareness and Engagement: A survey of site representatives revealed gaps in understanding and planning for network outages. ESnet responded by engaging with sites through meetings, calls, and visits to increase awareness and share best practices for network resilience.
- Data baselining: ESnet developed the Site Resilience Score to measure and track the resilience of each site’s connection. This involved updating databases and online portals to improve data accuracy and transparency. Preliminary analysis using this score has identified many sites where improvements are needed.
SRP staff also made progress on improving resilience at three specific sites by moving network connections and acquiring fiber to eliminate single points of failure. We will continue to work closely with sites to improve network resilience and ensure that ESnet can support the evolving needs of the DOE science community.
Stepping Up Our Trans-Atlantic Strategy
International connectivity has become essential for ESnet and our users, especially for researchers working on the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) projects. Transoceanic networking is prone to cable cuts and, because of the difficulty of repair, long resolution times. But laying a new cable across the Atlantic takes years of planning and hundreds of millions of dollars. Previously, ESnet contracted for lit circuits (for example, 100 Gbps wavelengths) across the ocean. This approach works well when bandwidth requirements are limited but does not scale sufficiently to the terabits of bandwidth needed for the coming High Luminosity upgrade of the LHC.
We switched our approach from lit circuits to optical spectrum, which will allow us to increase bandwidth more cost effectively and with greater control as optical networking technology evolves. Our plan set a target of at least 3.2 Tbps across four completely physically diverse paths, using cutting-edge optical spectrum services that will allow for long-term, cost-effective growth exceeding 10 Tbps. By doing this, anticipated traffic levels can be served well into the future for all ESnet sites, even during multiple outages.
In 2023, we began the design of and negotiation for our first such spectrum procurement. In early 2024, through an agreement with Aqua Comms, we acquired 25% of a fiber pair across the Atlantic that will enable us to configure 3 to 5 Tbps.
perfSONAR 5.0 Upgrades Performance Measurement and Monitoring
perfSONAR (perfsonar.net) is a platform for end-to-end network performance measurement and monitoring, deployed to over 2,000 installations across hundreds of networks on all seven continents. ESnet is a key member of the highly successful global perfSONAR collaboration.
In 2023, the perfSONAR project achieved a significant software development milestone with the release of version 5.0. This major release saw an overhaul of the perfSONAR storage backend, enabling richer analytics and visualization of perfSONAR data. It also aligned the architecture with ESnet’s Stardust platform, which simplifies correlation of additional network metrics such as flow data, traffic reports, and ticketing information.
Below is an example of a dashboard leveraging the new perfSONAR 5.0 backend to combine network flow data, ticketing information, and perfSONAR results into a single view. Views like this enable engineers to diagnose the impact and root cause quickly when performance problems are identified.
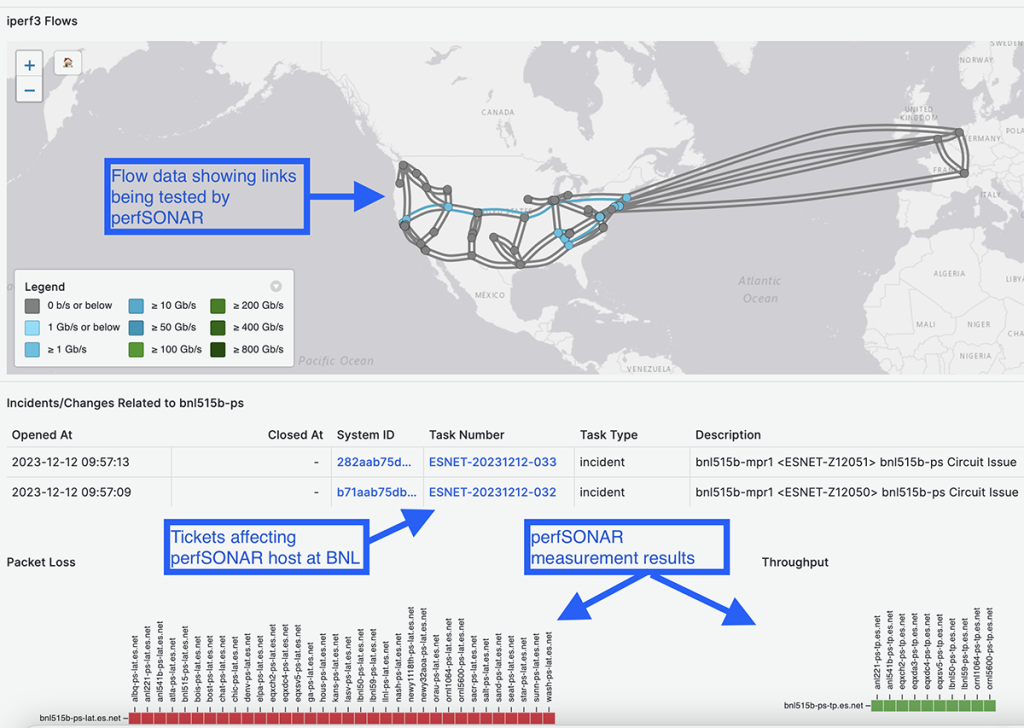
measurements with ESnet flow data and ticketing information.
iperf3 Release Supports Multithreading
ESnet has developed and refined many network diagnostic tools to ensure the optimal performance of the DOE’s high-speed network. These include iperf3, ESnet’s open-source bandwidth measurement tool for determining the maximum throughput between two hosts. The perfSONAR monitoring tool uses iperf3 in its test suite, and it is also used widely as a standalone tool for measuring network performance in general.
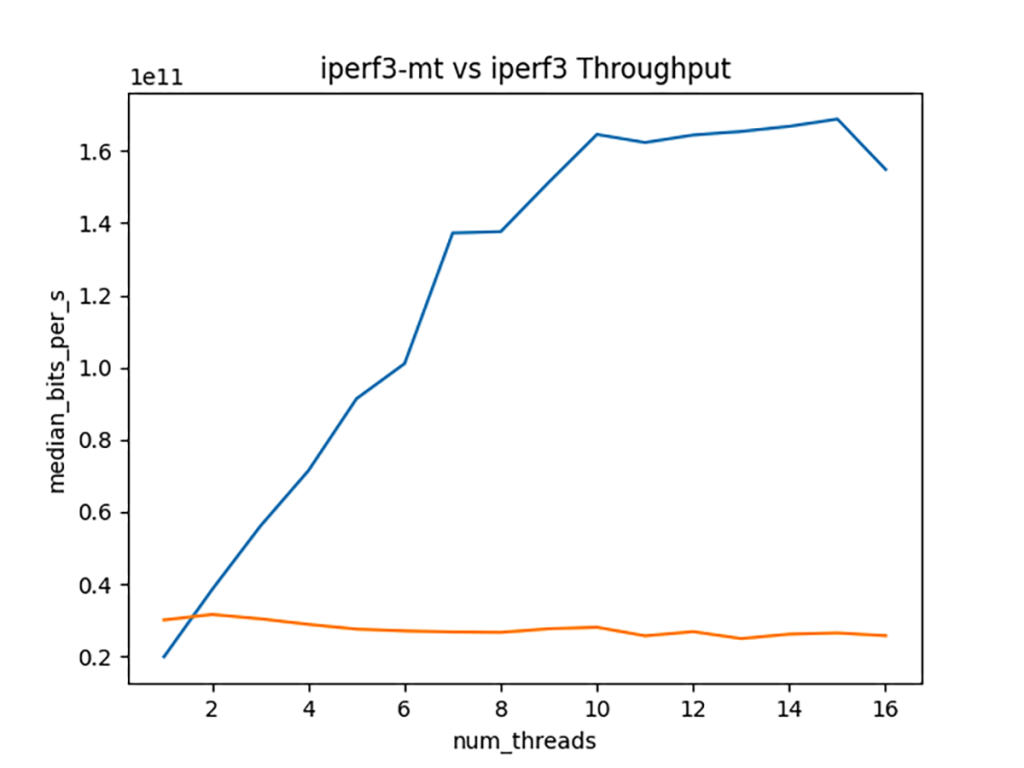
In November 2023, ESnet released iperf-3.16, which offers a significant improvement in handling multi-stream tests. iperf3 uses a separate thread and CPU core (if available) for each parallel stream in a test. This change improves iperf3’s ability to use and measure higher-speed network paths, particularly 100 Gbps and faster. This version has recorded transfers as fast as 148 Gbps in internal testing at ESnet over 200 Gbps paths.
This enhancement is essential to realizing the full potential of ESnet6, since many of its backbone links are 400 Gbps or faster. Performance bottlenecks in high-throughput networks are difficult to identify and troubleshoot without a tool that is capable of pushing the limits of a circuit. By providing more precise measurements and insights into network behavior, iperf-3.16 helps network engineers identify and address performance bottlenecks, ensuring fast, reliable data transfer for scientific collaborations that depend on it.
Grafana Accepts Sixth ESnet Plugin
ESnet’s Stardust is a time-series data collection, analysis, and visualization platform that provides a scalable means to collect and process multiple network measurements, allowing users to create custom dashboards and visuals. A public-facing component fosters collaboration with the global Research & Education (R&E) community.
The Stardust project team has made multiple open-source contributions in data visualization over the last few years, including a new one in 2023. This was an arc diagram developed by an ESnet student intern, which became our sixth plugin to be accepted by Grafana Labs, an open-source data-visualization ecosystem with more than 1 million active installations.
ESnet Leads Formation of MetrANOVA
In fall 2023, five members of the global R&E community agreed to form a measurement consortium, of which ESnet is the lead member. Participants worked throughout the year to secure resources to support the effort.

MetrANOVA (metranova.org) aims to be a neutral, trusted, and open consortium for Advancing Network Observation, Visualization, and Analysis. Its primary goal is to advance the state of measurement and analysis of national research and education networks by developing and socializing technical capabilities. Success will be based on member organizations and the broader community using these capabilities publicly and privately within their infrastructure. The consortium will focus on developing tools, tactics, and techniques that will help create more effective network measurement systems. Member organizations and the broader community are encouraged to use these resources to create appropriate local, distributed, and federated solutions.
Orchestrating and Automating Network Resources
A key objective of the ESnet6 project was the automated provisioning of network devices. This achievement was accomplished with the adoption and integration of the SURF Orchestrator and Cisco NSO products.
These investments increased in value in 2023 as ESnet refactored legacy applications to take advantage of the new capabilities and established formal relationships to support and promote the open-source Orchestrator project.
Major OSCARS Update
- Containerization: Aligning OSCARS with modern software practices for faster deployment and updates.
- Performance Boost: The OSCARS dependency libraries were modernized, resulting in an increase of 2,000 percent for path computation speeds. This reduced the time needed for worst-case pathfinding scenarios from approximately 1 minute to 3 seconds.
- Improved Communication: Seamless integration with Cisco NSO for smoother network automation.
- Live Status Monitoring: Real-time visibility within the user interface.
- Modernized User Interface: Enhanced usability and integration with Single Sign On (SSO) for improved security.
OSCARS (On-demand Secure Circuits and Advance Reservation System) is an advanced tool for scientists using ESnet, enabling them to quickly and easily reserve dedicated network resources for large data transfers. In 2023, ESnet significantly upgraded OSCARS, making it faster, more efficient, and easier to use. Key improvements include:
Sharing the Workflow Orchestrator
ESnet continued to collaborate with international partners to advance the development and adoption of Workflow Orchestrator. This powerful open-source software platform for automating the provisioning of network services was first developed by SURF, the Netherlands’ NREN. ESnet teamed up with SURF to open source the project and adapt it for our own use as well as other NRENs. In 2023, SURF and ESnet led Workflow Orchestrator workshops around the world, resulting in Europe’s GÉANT and Ireland’s HEAnet joining the collaboration. ESnet also met with the Australian and Canadian NRENs AARnet and CANARIE, which have expressed interest in joining the collaboration. These efforts demonstrate ESnet’s commitment to fostering a global community to share knowledge and advance the capabilities of research and education networks worldwide.
Meeting the Security Targets for Zero Trust
The U.S. federal government announced in January 2022 that its agencies must meet specific cybersecurity standards and objectives aligned with a Zero Trust architecture by the end of fiscal 2024. Zero Trust is an approach to cybersecurity that goes beyond “trust but verify” and treats all networks and traffic as potential threats.
ESnet’s Security team has approached Zero Trust as a framework and set of architectural design principles that assume an adversary has access to its internal networks. Zero Trust mitigates this risk by moving focus away from brittle network perimeters and toward individual sessions between users, assets, and resources. There is no implicit trust based solely on an asset’s network location or ownership. Greater robustness and resilience are then achieved by limiting the impacts of the compromise of an individual system.
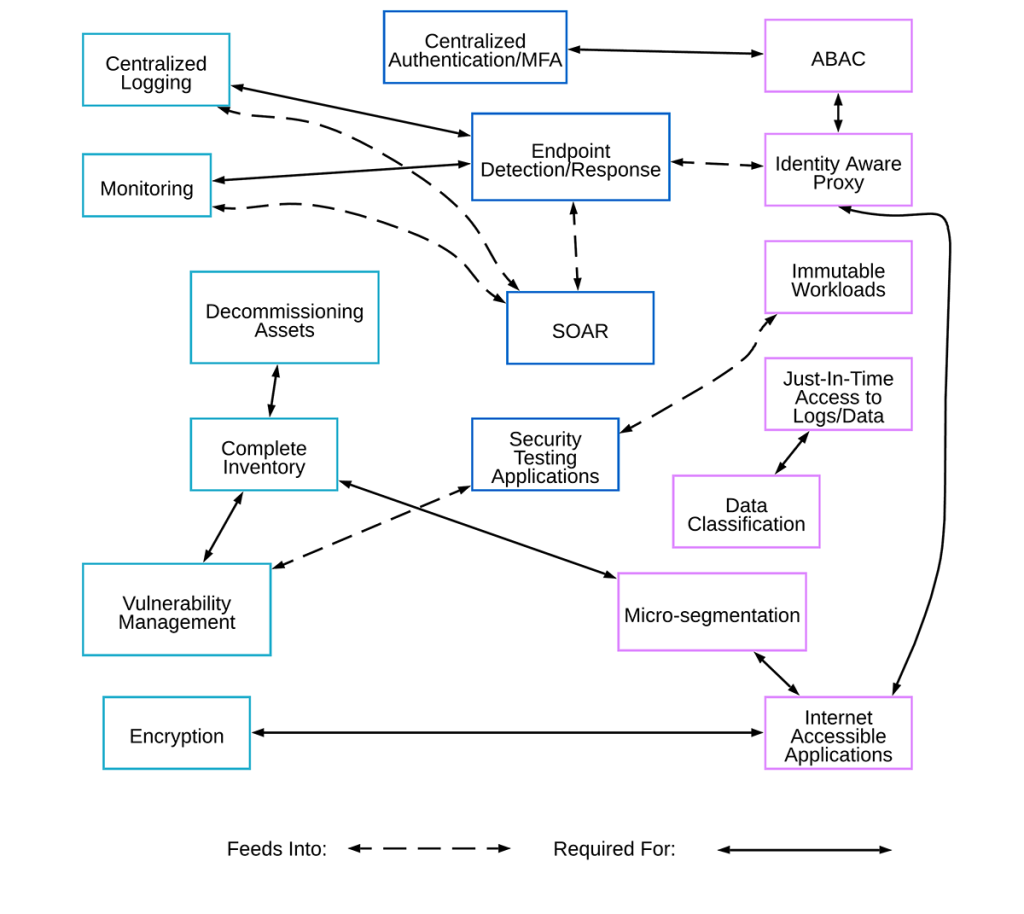
In February 2023, ESnet formed a Zero Trust Working Group (ZTWG) with members from across the organization. This group’s directive is to translate each of the 15 domains (see figure) into a set of prioritized plans. The ZTWG meets regularly to develop architectures and detailed requirements by organizing and forming a number of smaller domain teams responsible for translating the components of these domains into technical requirements and architectures for ESnet.
Since the ZTWG began meeting, several domain teams have been formed. Each has worked to carefully define the requirements, create a framework from which gaps can be identified, and determine how the requirements for new projects to address those gaps are set. From here, new project teams are spun up. The first such project in 2023 was to identify all web services not using ESnet Single Sign On (SSO) and to begin migrating those services away from local credentials and to a multi-factor SSO tied to ESnet’s authorizations systems and off-boarding processes.
In 2024, we will transition into the second phase of our Zero Trust initiative, adding a focus on authorization for access and services, centralized logging at all levels, and full intra-datacenter encryption.
